In severe internal diseases, poor nutrition, as well as with age, the growth of the nail slows down, its structure undergoes changes. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of the disorder based on the results of tests and microscopic examinations.
But to get an idea of what happens to toenails or toenails, you can use the photo with fungal diseases of various kinds.
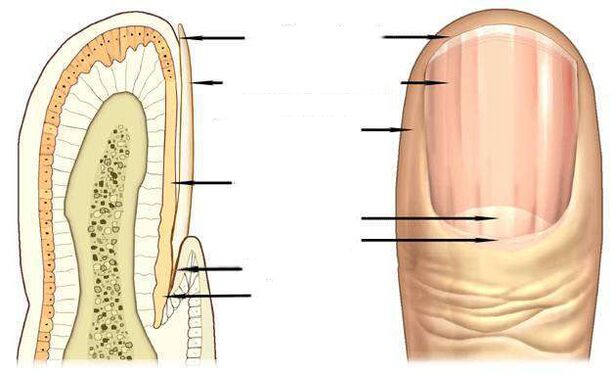
Causes of nail deformity
Molds, yeast-like fungi and dermatophyte fungi cause infectious nail diseases (onychomycosis) that show similar symptoms.
All types of toenail fungus deform the nail plate, change its transparency, shine, color, this variety can be seen in the presented photos.
Changes in the nail occur not only in onychomycosis, but also in injuries, chronic paronychia (inflammation of the nail fold), psoriasis, eczema on the hands, dermatitis. Before concluding that there is a fungal infection, you should consider all possible options.
Signs of fungal infection
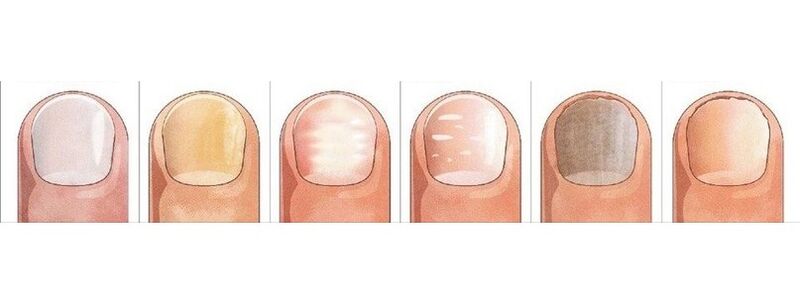
The most informative signs of fungal infection are changes in the color of the nail plate, the presence of peeling nails, superficial changes - transverse, longitudinal grooves of the nail plate, point indentations, thickening, destruction of the nail.
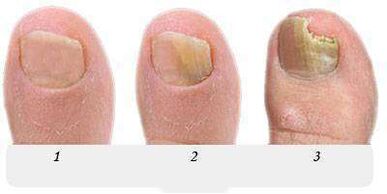
The pink color of a healthy nail is determined by the transparency of the nail plate and the blood vessels visible through it. In onychomycosis the nail loses its transparency, the color becomes brownish, yellow, rarely green, black.
The fungus Candida and dermatophytes cause onycholysis - the separation of the affected part of the nail. When infected with dermatophytes, onycholysis is observed from the distal edge of the nail, and when infected with Candida, the nail lags behind the nail bed at the base, in the area of the crescent.
A symptom of candidal fungus can be inflammation of the lateral peringual ridges - paronychia. This disease has bacterial forms caused by streptococci and staphylococci, as well as non-infectious - eczema, psoriasis, systemic vasculitis.
When the toenails are affected by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum, the plate is affected, as you can see in the picture, the roller is not affected by the infection. The plate becomes yellowish, thickens strongly, the accumulated fungal masses differ well below it.
Nail fungus due to dermatophyte infection
In 95% of all cases of nail fungus, the disease is caused by dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
Infection with Trichophyton rubrum
Onychomycosis begins when the fungus penetrates under the nail plate from the free edge. The fungal infection is indicated by the appearance of a yellowish spot, an uneven, crumbling surface on the distal (distant) edge of the nail in the area of the spot.
distal-lateral formof dermatophyte fungal infection with Trichophyton rubrum is common. In the photo you can see that the stain caused by the introduction of the fungus is located along the lateral peringual fold of the nail.
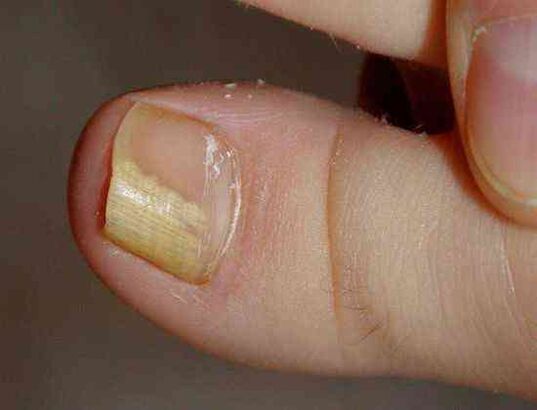
The fungus Trichophyton rubrum usually affects the big toes, causing hyperkeratosis - an accumulation of fungus between the nail plate and the nail bed, which looks like a loose yellowish mass in the photo.
At this stage, the fungus occupies an insignificant part of the nail, as in the photo presented, and with the help of local treatment it is possible to deal with the beginner onychomycosis.
Without treatment, the spot grows, gradually affects the entire edge of the nail and then moves to the crescent. In the photo, the nail fungus looks like yellowish streaks directed towards the area of growth of the nail plate.
In thedistal form of nail fungus, which is often found on the big toes, on the distal edge of the nail, in its central part, yellowish spots of infection appear, as can be seenon the picture.
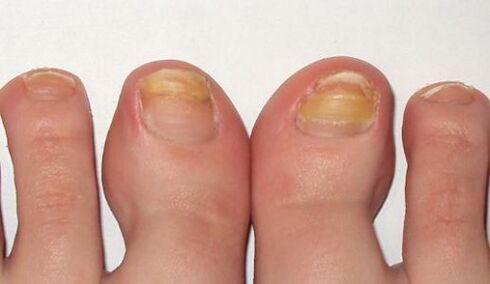
In the advanced stage of the fungus on the feet, several nails are affected, as in the picture, and treatment is no longer limited to topical remedies and pills. In addition to antifungal drugs, the nail is subjected to hardware cleaning to completely or partially remove the nail plate.
Long-term therapy using all known antifungal agents and treatments should be performed on the legs caused by Trichophyton rubrum, with hyperkeritosis, as seen in the photo.
Fungal infection with general nail damage spreads over the entire area of the nail plate, the nail is completely destroyed.
Infection with another dermatophyte, the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes, can also lead to a total fungal infection of the nail.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection
In case of total defeat of the toenail with the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes, the nail plate is deformed, the photo shows that it thickens, changes its structure, collapses, yellowish spots appear on its entire surface.
Infection of the nail with this dermatophyte usually causes superficial white onychomycosis of the big toe, less often of the little finger.
This fungus practically does not appear on the nails of the hands, often causes interdigital dermatophytosis of the feet, as in the picture, and requires simultaneous treatment of the skin of the feet and nails.
A symptom of a fungal infection on the nails, usually on the feet, are white spots of various sizes, as in the picture, reminiscent of leukonychia - a disease of the nail plate itself.
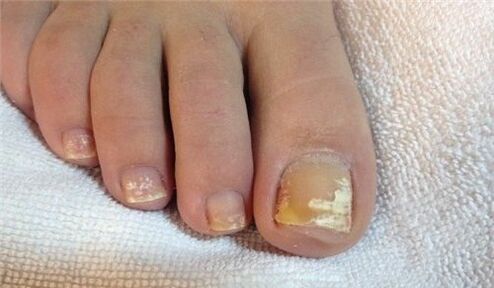
But unlike leukonychia, in which white spots are caused by the appearance of air bubbles in the layers of the nail, white spots in a fungal infection are the result of the activity of Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
Rarely, superficial white onychomycosis is caused by mold; in AIDS, the causative agent of this type of fungus can be Trichophyton rubrum and affect the nails of both feet and hands.
Nail changes due to Candida infection
The fungus usually occurs in women, affecting the nails of the working hand, which is more often in contact with water.
Candidal onychomycosis is characterized by a proximal form of infection in which the fungus first affects the nail fold at the base of the nail and then penetrates the growth zone and the nail bed. It then gradually moves along the nail from the base to the edge, capturing an increasing area of the nail plate.
The causative agent of candidal onychomycosis is Candida albicans. This fungus invades the fingernails and toenails, spreading from the crescent at the base of the nail plate to the free edge, as can be seen in the photo.
A sign of Candida nail infectionalbicans is inflammation of the nail fold (paronychia), separation of the cuticle from the nail plate, pain, discharge of pus when a bacterial infection is attached.
Candida albicans is able to penetrate the nail and from its free edge. In this case, they talk about the distal form of infection, which is combined, as a rule, with cutaneous candidiasis.
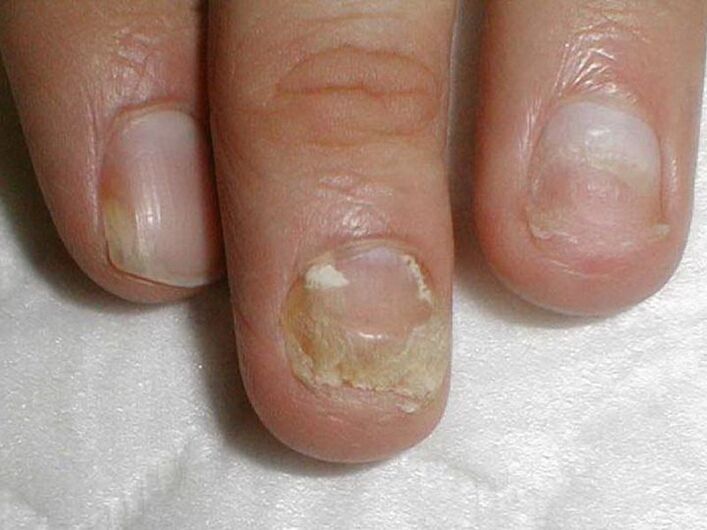
Treatment of Candida fungus on the nails of the hands and feet with damage to more than half of the area of the nail plate, as pictured, includes not only the fight against onychomycosis, but also measures to reduce the activity of Candida inthe natural reservoirs for their storage - the intestines, the oral cavity, the genital mucosa. . .
Mold attack
Molds cause fungus much less frequently than Candida or dermatophytes. The main symptom of a nail infection with mold is, as you can see in the picture, achange in the color of the nail plate to blue, black, greenish.
Signs of nail mold on the nails can be dark spots, dots on the nail plate or, as in the picture, a black longitudinal stripe.
Antifungal preparations
Antifungals with fluconazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine, itraconazole, griseofulvin are used to treat nail fungus caused by dermatophytes, such as in this photo.
Antifungals with terbinafine are effective in dermatophyte infections.
Antifungal agents with voriconazole are highly active against dermatophytes.
Itis also usedto treat nail moldon the feet, hands andagainst Candida yeast. The spectrum of action includes molds such as Aspergillum, Fusarium, Penicillium.
Itraconazole-based preparations deal with mold.
Fungal nail diseases
Occasionally there is a grayish tingeon the nailwith eczema. In this case, the nail plate may move away from the nail bed, which is observed in fungi.
Externally very similar to onychomycosismanifestations of psoriasis. In this disease, not only doesthe color change, but alsothe nail plate thickens.
Point indentations are found on its surface, separation of the nail plate from the nail bed is noted. But there are differences from the fungus: in psoriasis, the separated and healthy parts of the toenail are separated with a pink, yellowish band over time.
Bluish colorgets the nailwith pseudomonas nail infection. Frequent mechanical friction of the nail fold causes the appearance of superficial grooves, wavyness of the nail.
White spots of leukonychia, the appearance of whichis associated with metabolic disorders, can also be confused with a superficial white sponge with a large spot area.
Changes in the color, shape of the nail, causing injury. The big toes are at greatest risk. The nail with injury, as well as with fungus, thickens and darkens.

The difference between the injury and the fungus is that the changes during the injury are noted only on the damaged finger, the nails of the other fingers remain unchanged, they are not infected by the diseased finger, as in onychomycosis.
The consequence of the trauma can be a partial separation of the nail from the nail bed, the formation of a cavity, which under adverse conditions is quickly colonized by fungi.
The nail plate can be separated from the nail bed under the influence of light (photonicholysis), in iron deficiency anemia, hormonal diseases. Splitting, nail loss occurs with lichen erythematosus, bullous dermatoses, nail trauma.
But finally you can be sure that the conclusion is correct and start treatment only after seeking help from a dermatologist - a specialist in skin diseases or mycologist - a doctor who treats fungal diseases.





























